Sustainable Semiconductors: R&D Progress & Barriers
The semiconductor industry plays a crucial role in modern technology, but its environmental impact has become an increasing concern. Developing sustainable semiconductors that minimize environmental impact while maintaining high performance is essential for the industry’s future.
This article discusses the progress made in creating sustainable semiconductors, the challenges faced, and the opportunities available for research and development (R&D) professionals.
What are Sustainable Semiconductors?
Sustainable semiconductors refer to semiconductor materials, devices, and manufacturing processes that prioritize environmental sustainability and minimize their impact on the planet.
The semiconductor industry plays a crucial role in various technologies, including electronics, computing, renewable energy, and communication systems. Making semiconductors more sustainable involves considering the entire lifecycle of semiconductor products, from raw material extraction to manufacturing, usage, and disposal.
Progress in Sustainable Semiconductors
There has been significant progress in the development of sustainable semiconductors. Some notable advancements include:
- Energy-Efficient Technologies: Reducing energy consumption in semiconductor fabrication processes has been a major focus, with the adoption of energy-efficient technologies such as advanced process control, novel lithography techniques, and waste heat recovery systems.
- Alternative Materials: Researchers have been exploring alternative materials, such as organic and two-dimensional (2D) materials, which offer benefits like lower processing temperatures, reduced waste, and improved recyclability.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable manufacturing practices, including water recycling, waste reduction, and the use of renewable energy sources.
Barriers to Sustainable Semiconductors
Despite progress, several barriers still hinder the development of sustainable semiconductors. These include:
Technological Challenges: Developing sustainable alternatives to traditional materials and processes can be challenging due to the need to maintain or improve performance while minimizing environmental impact.
Economic Factors: The high costs associated with adopting sustainable technologies and materials can deter companies from investing in such initiatives.
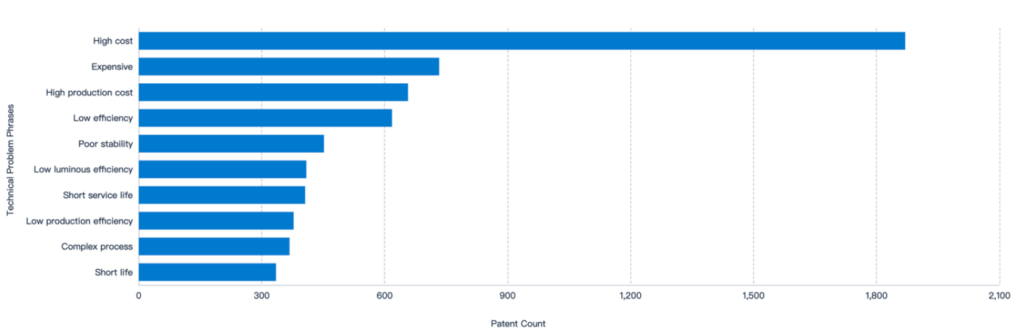
Since new alternatives are in their early stages, they are often more expensive. Therefore, R&D teams are focusing on finding ways to reduce the cost of sustainable alternatives.
Limited Industry Collaboration: The competitive nature of the semiconductor industry can hinder collaboration and knowledge sharing, which are essential for developing and adopting sustainable solutions.
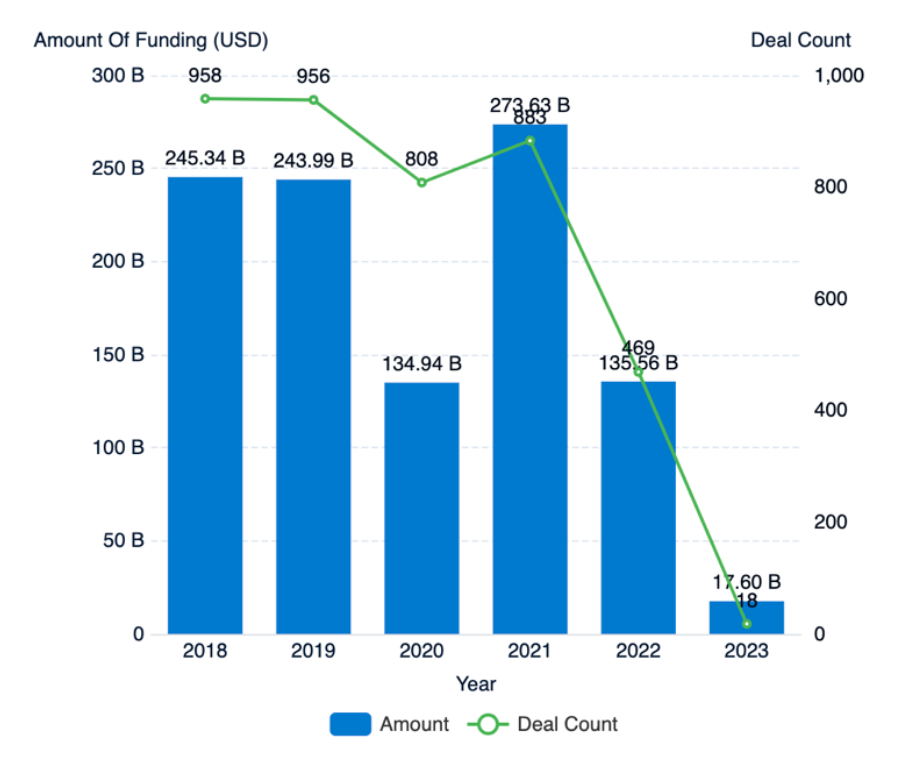
Investment in the semiconductor industry peaked in 2021 with 883 deals totaling $273.63 billion, but since then, there has been a decline in M&A activity. This reduced collaboration makes it difficult for companies to develop new technologies quickly, particularly as semiconductor supply shortages persist. Even with collaboration, the slow pace of innovation hampers progress in the industry.
Opportunities for R&D Professionals
There are numerous opportunities for R&D professionals to contribute to the development of sustainable semiconductors:
- Material Innovation: Developing innovative materials with reduced environmental impact, such as organic semiconductors, perovskites, and 2D materials, offers significant opportunities for R&D.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Researching and developing novel manufacturing techniques that reduce energy consumption, waste generation, and chemical usage can lead to more sustainable semiconductor production.
- Circular Economy Models: Exploring circular economy models, which focus on the reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials, can help minimize the environmental impact of the semiconductor industry.
Closing Thoughts
R&D professionals have a crucial role to play in driving the development of sustainable semiconductors, with opportunities to innovate in materials, manufacturing techniques, and circular economy models. As the industry continues to evolve, the focus on sustainability will become increasingly important, ensuring a more environmentally responsible and economically viable future for the semiconductor industry.
Your recommended content
-

Patsnap Releases 2023 Global Innovation Report: The Brilliant Names to the Dynamic Landscape of Innovation
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Research Tag | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
The Global Innovation 100 and Global Disruption 50 transcend individual entities, each representing a small innovation ecosystem with numerous subsidiaries. Through the innovation data of these companies, we gain insights into the characteristics, structures, and trends of global innovation.
-

Patsnap’s 2023 Disruption 50: A Closer Look at Tomorrow’s Innovators
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Research Tag | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Through active growth, the Global Disruption 50 have quickly established solid technology quality and profound technology influence that are comparable to that of the Global Innovation 100.
-

Impact of Patsnap’s 2023 Global Disruption 50
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
The 2023 Global Disruption 50, 30% of which come from the Information Technology sector, are shifting the world’s innovation focus from a physical world of Atoms, to a digital world of Bits, and then a “world of Atoms empowered by Bits”.
