How MIT is Using AI to Combat Superbugs
An electrifying study conducted by leading scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is stirring up the medical research community. Their exploration zeroes in on how artificial intelligence (AI) can become a potent ally in creating new antibiotics to challenge drug-resistant bacteria.
In this article, we’ll explore what superbugs are, why they’re dangerous, and how scientists are using AI to combat them.
Jump to . . .
- What are Superbugs?
- How do Superbugs Occur?
- Why is Finding a Treatment Important?
- How MIT is Using AI to Combat Superbugs
- Closing Thoughts
What are Superbugs?
Superbugs are strains of bacteria that have developed resistance to multiple antibiotics. They are often a result of the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in human healthcare, agriculture, and veterinary practices. Through a process called genetic mutation or acquiring resistance genes from other bacteria, these pathogens can evolve and render antibiotics ineffective.
How do Superbugs Occur?
The misuse of antibiotics has fueled the rise of superbugs. Overprescribing antibiotics, patients not completing their full course of treatment, and the use of antibiotics in livestock farming all contribute to the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. As a result, once-treatable infections become difficult, and sometimes impossible, to control.
Why is Finding a Treatment Important?
Effective treatment options for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are not only critical for patient well-being but also carry significant economic implications. If left unaddressed, AMR is projected to surpass cancer as a leading cause of death, accounting for approximately 10 million fatalities annually by 2050.
Presently, drug-resistant infections claim the lives of around 700,000 individuals each year. The economic toll of AMR could reach a staggering $100 trillion globally by 2050, while simultaneously pushing an additional 28 million people into poverty. Combating AMR and finding sustainable solutions is not only a matter of public health but also of immense economic importance.
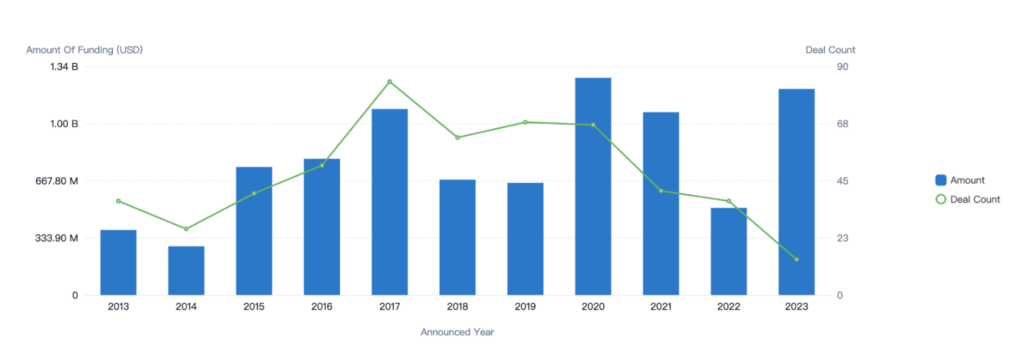
The graph above depicts a notable increase in VC deals focused on antibiotic-resistant treatment this year, signaling a renewed surge of interest in the field.
How MIT is Using AI to Combat Superbugs
A recent study conducted by MIT zeroes in on how AI can become a potent ally in creating new antibiotics to challenge drug-resistant bacteria.
Harnessing the computational power of AI algorithms, the MIT team processed a colossal trove of data, sifting through complex molecular structures to pinpoint potential drug candidates. This revolutionary approach, coined “in-silico” drug discovery, turbocharges the drug development process and equips scientists to precisely target and neutralize stubborn bacteria that have learned to shrug off traditional antibiotics.
Using AI, MIT scientists successfully pinpointed a compound with the ability to eliminate Acinetobacter baumannii, a notorious bacterium commonly found in hospital environments. This bacterium is known for its ability to cause various infections, ranging from mild to severe, and it has become a major concern in healthcare settings.
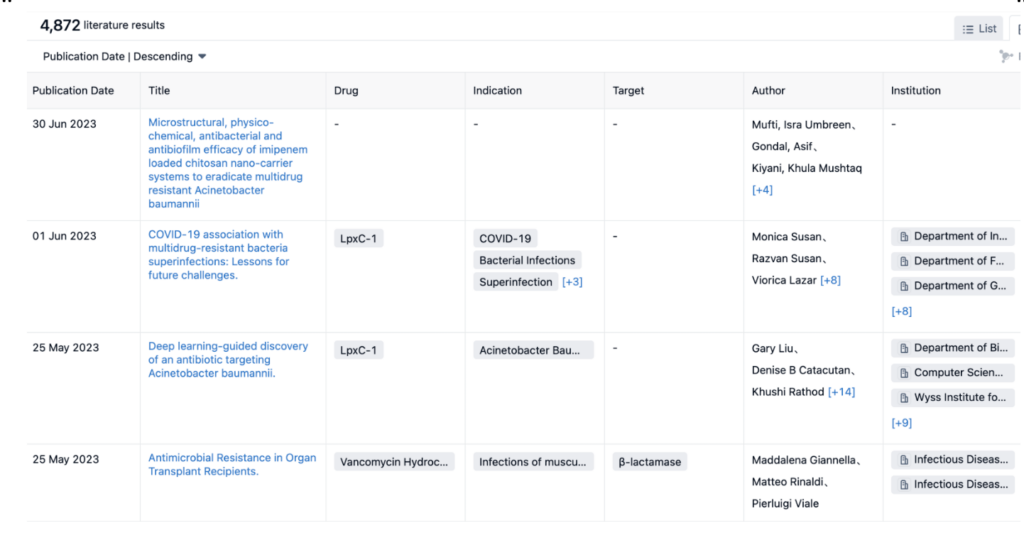
As the image above shows, the number of literature results surrounding the topic of the Acinetobacter baumannii bacterium. From Patsnap’s Synapse platform, there are just under 5000 literature results, indicating that this bacterium is of high interest at the moment. Researchers are battling it out to find a solution to this superbug and prevent the continued threat it poses to the human population.
One of the primary concerns is its propensity to cause healthcare-associated infections, including bloodstream infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and surgical site infections. These infections can be challenging to treat due to the bacterium’s natural resilience and its ability to develop resistance to multiple antibiotics.
Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing intensive care treatment or with underlying health conditions, are particularly susceptible to Acinetobacter baumannii infections. In these vulnerable populations, the impact of the bacterium can be even more severe, leading to higher morbidity and mortality rates. Acinetobacter baumannii also spreads easily between patients, especially in settings with inadequate infection control measures. This can result in outbreaks and contribute to the overall burden of healthcare-associated infections.
Closing Thoughts: Embracing the Future of AI-Powered Drug Discovery and Development
This innovative application of AI in the medical industry exemplifies the transformative role technology can play in addressing critical healthcare challenges. By leveraging advanced algorithms and computational power, researchers are unlocking new avenues for medical breakthroughs that were once unimaginable.
From a patient perspective, AI-powered drug discovery holds the promise of accelerating the availability of life-saving treatments. By expediting the identification and development of novel therapies, such as effective treatment for superbugs, patients can benefit from quicker access to innovative medications.
Your recommended content
-

Patsnap Releases 2023 Global Innovation Report: The Brilliant Names to the Dynamic Landscape of Innovation
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Research Tag | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
The Global Innovation 100 and Global Disruption 50 transcend individual entities, each representing a small innovation ecosystem with numerous subsidiaries. Through the innovation data of these companies, we gain insights into the characteristics, structures, and trends of global innovation.
-

Patsnap’s 2023 Disruption 50: A Closer Look at Tomorrow’s Innovators
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Research Tag | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Through active growth, the Global Disruption 50 have quickly established solid technology quality and profound technology influence that are comparable to that of the Global Innovation 100.
-

Impact of Patsnap’s 2023 Global Disruption 50
Category: Article | Category: eBook | Category: Whitepaper
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
The 2023 Global Disruption 50, 30% of which come from the Information Technology sector, are shifting the world’s innovation focus from a physical world of Atoms, to a digital world of Bits, and then a “world of Atoms empowered by Bits”.
